

Firs (Abies spp.) are keystone components of the boreal and temperate dark-coniferous forests and this genus harbors a number of relict taxa. Wei et al. (pages 2664–2682) reconstructed a transcriptomebased phylogeny and revealed the spatiotemporal evolution of global firs based on complete species sampling. Evolutionary and ecological analyses indicate that all extant firs underwent diversification in the Late Cenozoic, with the species richness distribution driven primarily by elevation and precipitation of the coldest quarter. Some morphological traits linked to elevational variation and cold tolerance may have contributed to the diversification of global firs. This work may inform forest management and species conservation in a warming world. The cover shows the dark blue cones of an alpine fir (Abies georgei var. smithii).
Brief Communications
Two-faced OsNAS₃ influences disease resistance via nicotianamine and ethylene
Kaiwei He, Liting Xu, Qin He, Wei Zhang, Ying Zhang, Xiaobo Zhu, Junjie Yin, Qing Xiong, Qingqing Hou, Yongyan Tang, Min He, Xuewei Chen, Weitao Li

The loss and gain ofOsNAS₃function both positively influence plant disease resistance. Overexpression ofOsNAS₃boosts blast resistance by promoting nicotianamine accumulation, thereby enhancing blast resistance. Conversely, knockout ofOsNAS₃increases ethylene biosynthesis, also contributing to improved blast resistance.
Review Article
Reading m⁶A marks in mRNA: A potent mechanism of gene regulation in plants
Thi Kim Hang Nguyen, Hunseung Kang

This review examines N6-methyladenosine (m⁶A) metabolism, including how m⁶A readers, writers, and erasers recognize and interpret m⁶A modification on mRNAs; how they regulate the stability, splicing, transport, and translation of mRNAs; and how they function in the response of plants to developmental and environmental signals.
Abiotic Stress Responses
HOS1 ubiquitinates SPL9 for degradation to modulate salinity-delayed flowering
Zhixin Jiao, Xiaoning Shi, Rui Xu, Mingxia Zhang, Leelyn Chong, Yingfang Zhu

The nuclear pore complex component HIGH EXPRESSION OF OSMOTICALLY RESPONSIVE GENE 1 ubiquitinates SQUAMOSA PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE 9 in the regulation of a key adaptive response to environmental stress, delayed flowering in response to high salinity.
Cell and Developmental Biology
The METHYLTRANSFERASE B–SERRATE interaction mediates the reciprocal regulation of microRNA biogenesis and RNA m6A modification
Haiyan Bai, Yanghuan Dai, Panting Fan, Yiming Zhou, Xiangying Wang, Jingjing Chen, Yuzhe Jiao, Chang Du, Zhuoxi Huang, Yuting Xie, Xiaoyu Guo, Xiaoqiang Lang, Yongqing Ling, Yizhen Deng, Qi Liu, Shengbo He, Zhonghui Zhang

InArabidopsis, METHYLTRANSFERASE B (MTB)–SERRATE (SE) interaction links RNA m6A methylase complex and microprocessor, affecting microRNA production and m6A modification. Knockdown of MTB impairs microRNA biogenesis and loss of SE function disrupts transcriptome-wide m6A modification. SE enhances the liquid-liquid phase separation and solubility of the m6A methylase complex.
GhCASPL1 regulates secondary cell wall thickening in cotton fibers by stabilizing the cellulose synthase complex on the plasma membrane
Li Zhang, Xingpeng Wen, Xin Chen, Yifan Zhou, Kun Wang, Yuxian Zhu

The cellulose synthase complex–interacting factor CASPARIAN STRIP MEMBRANE DOMAIN-LIKE1 plays a crucial role in regulating secondary cell wall thickening in cotton fibers by stabilizing the cellulose synthase complex on the plasma membrane.
The OsMAPK5–OsWRKY72 module negatively regulates grain length and grain weight in rice
Fuxiang Wang, Jiexin Lin, Fan Yang, Xiaofeng Chen, Yiyi Liu, Lingnan Yan, Jing Chen, Zonghua Wang, Huaan Xie, Jianfu Zhang, Huibin Xu, Songbiao Chen

The kinase OsMAPK5 interacts with the kinases OsMAPKK3/4/5 and the transcription factor OsWRKY72 and phosphorylates OsWRKY72. OsWRKY72 targets the W-box motifs in the promoter of the auxin-response factor geneOsARF6to activateOsARF6expression, thereby modulating auxin responses and negatively regulating grain length and grain weight in rice.
Molecular Ecology and Evolution
Phylotranscriptomic and ecological analyses reveal the evolution and morphological adaptation ofAbies
Zhou-Rui Wei, Dan Jiao, Christian Anton Wehenkel, Xiao-Xin Wei, Xiao-Quan Wang

A transcriptome-based phylogeny based on complete species sampling revealed the spatiotemporal evolution of global firs (Abiesspp.). Evolutionary and ecological analyses indicate a diversification of all extant firs in the Late Cenozoic, with the species richness distribution driven primarily by elevation range and precipitation of the coldest quarter.
Molecular Physiology
Sucrose induces flowering by degradation of the floral repressor Ghd7 via K48-linked polyubiquitination in rice
Lae-Hyeon Cho, Jinmi Yoon, Gibeom Baek, Win Tun, Hyeok Chan Kwon, Dae-Woo Lee, Seok-Hyun Choi, Yang-Seok Lee, Jong-Seong Jeon, Gynheung An

In response to sucrose, the E3 ligase IDEAL PLANT ARCHITECTURE 1 INTERACTOR 1 mediates the K48-linked polyubiquitination of the flowering repressor Grain and heading date 7, leading to its degradation and thereby accelerating flowering in rice.
The miR396a–SlGRF8 module regulates sugar accumulation in the roots via SlSTP10 during the interaction between root-knot nematodes and tomato plants
Lulu Sun, Mengting Zhu, Xiaoxuan Zhou, Ruiyue Gu, Yuying Hou, Tongtong Li, Huang Huang, Rui Yang, Shaohui Wang, Wenchao Zhao

A potential regulatory model for sugar redistribution mediated by the microRNA miR396a, the growth-regulating factor SlGRF8, and the sugar transporter SlSTP10 during tomato-root-knot nematode interactions provides a theoretical basis for understanding sugar competition during plant-parasitic nematode interactions.
Functional Omics and Systems Biology
Haplotype-resolved genome of a heterozygous wild peach reveals thePdaWRKY4-PdaCYP716A1module mediates resistance to aphids by regulating betulin biosynthesis
Jun-Xiu Wang, Yong Li, Xin-Wei Wang, Ke Cao, Chang-Wen Chen, Jin-Long Wu, Wei-Chao Fang, Geng-Rui Zhu, Xue-Jia Chen, Dan-Dan Guo, Jiao Wang, Ya-Lin Zhao, Jia-Qi Fan, Su-Ning Liu, Wen-Qing Li, Hang-Ling Bie, Qiang Xu, Li-Rong Wang

Haploid genome assembly and population analysis of the wild peach Prunus davidiana identified a key aphid-resistance gene,PdaWRKY4, with a 9-bp deletion in its promoter enhancing its expression in aphid-resistant plants. PdaWRKY4 regulates aphid resistance by promoting PdaCYP716A1-mediated biosynthesis of the anti-aphid metabolite botulin.
How have breeders adapted rice flowering to the growing region?
Asako Kobayashi, Mao Suganami, Hideki Yoshida, Yoichi Morinaka, Syuto Watanabe, Yoshie Machida, Genki Chaya, Fumihiro Nakaoka, Nobuhito Sato, Kotaro Miura, Makoto Matsuoka

Rice breeders use their experience and intuition to develop varieties with the optimum heading date for different growing areas; genome-wide association studies and partial correlation analysis showed that Japanese breeders have achieved the desired heading date by cleverly combining four specificHeading date(Hd) genes,Hd1,Hd16,Hd17, andHd18.
Plant Biotic Interactions
The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase OsBSK1-2 regulates immunity via an HLH/bHLH complex
Xun Wang, Zhijuan Diao, Chang Cao, Yan Liu, Na Xia, Youlian Zhang, Ling Lu, Fanyu Kong, Houli Zhou, Lizhe Chen, Jing Zhang, Bangsheng Wang, Ronghua Huang, Dingzhong Tang, Shengping Li
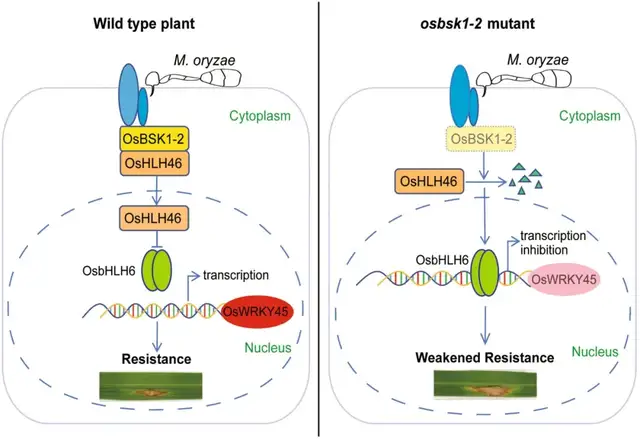
The receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase OsBSK1-2 positively regulates rice blast resistance by stabilizing the atypical bHLH transcription factor OsHLH46. OsHLH46 interacts with and inhibits the function of OsbHLH6, a negative immune regulator, by suppressing its transcriptional inhibition of the positive immune regulatorOsWRKY45.
