

Tea-oil pollen toxic to honeybee larvae:When honeybees forage on the flowers ofCamellia oleifera, a widely planted oilseed crop, their larvae die, but what kills the larvae remains controversial. Using bagging and caging studies, the authors show that birds effectively pollinateC. oleiferaflowers. In contrast to the hypothesis of nectar toxicity, Zhang et al. (pages 2313-2316) propose thatC. oleiferamay have evolved toxic pollen to limit overexploitation of its pollen by bees. Toxicity tests indicated thatC. oleiferapollen harmed honeybee larvae significantly more than pollen fromBrassica napus, another oilseed crop, andC. oleiferapollen contains the insecticidal compound theasaponin. The cover shows simultaneous pollen presentation in aC. oleiferaflower.
Commentary
Why is pollen inCamellia oleiferainedible to honeybees?
Jannathan Mamut, Wei-Bing Zhang, Lu-Lu Tang

This Commentary examines a recent study that addressed a long-standing controversy: Is the lethal effect of Tea-oil Camellia on honeybee larvae due to nectar or pollen toxicity? Flowers ofCamellia oleiferaare adapting to bird pollination, evolving ‘anti-bee’ traits such as theasaponin-containing pollen, which is toxic to bee larvae.
News and Views
New perspective on pollen toxicity inCamellia oleifera
Bin Yuan, Xiao-ming Fan, Fu-liang Hu, Yi-bo Luo

Exploring pollen chemical defenses in the economically important plantCamellia oleiferaand examining their effects on honeybee flower-visiting behavior improves the understanding of the ecological functions of pollen and informs efforts to manage honeybees to bolsterC. oleiferaproduction.
Brief Communications
Lethal effects of tea-oilCamelliaon honeybee larvae due to pollen toxicity
Chuan Zhang, Hui-Hui Feng, Ya-Lei Liu, Shuang-Quan Huang

Toxicity tests on tea-oilCamelliaflowers (Camellia oleifera) indicated that its pollen harmed honeybee larvae significantly more than pollen from oilseed rape (Brassica napus) flowers. TheC. oleiferapollen contained high levels of the toxic triterpenoid theasaponin, which was undetectable in nectar.
Generation of humidity-sensitive genic male sterility in maize and wheat for hybrid seed production
Xingchen Xiong, Dan Wang, Changfeng Guo, Guiqiang Fan, Yingchun Zhang, Bo Song, Bingzhu Hou, Yuanyuan Yan, Chuanxiao Xie, Xiaoduo Lu, Chunyi Zhang, Xiaoquan Qi

Loss of function of a conserved POACEATAPETOL SYNTHASE1 confers humidity sensitive genic male sterility in maize and wheat. This system yielded >99% pure hybrid seed in maize.
Tradeoff between productivity and stability across above- and below-ground communities
Zonghao Hu, Haiyan Liu, Junjie Yang, Bin Hua, Michael Bahn, Shuang Pang, Tingting Li, Wei Yang, Honghui Wu, Xingguo Han, Ximei Zhang

An 11-year nitrogen addition experiment reveals that for both plants and soil microorganisms, the ruderal strategists had higher productivity but lower stability, while the tolerant strategists had higher stability and lower productivity, leading to the tradeoff between productivity and stability within and across above- and below-ground communities.
OsFAD1–OsMYBR22modulates clustered spikelet through regulatingBRD3in rice
Mingxing Cheng, Huanran Yuan, Ruihua Wang, Fengfeng Fan, Fengfeng Si, Xiong Luo, Wei Liu, Shaoqing Li

The phenotype of riceclustered spikeletmutants results from the upregulation of the FAD/NAD(P)-binding oxidoreductase family geneOsFAD1. Enhanced interaction between OsFAD1 and the transcription factor OsMYBR22 leads to the upregulation of the spikelet clustering-related BR catabolic geneBRD3.
New Technology
MetMiner: A user-friendly pipeline for large-scale plant metabolomics data analysis
Xiao Wang, Shuang Liang, Wenqi Yang, Ke Yu, Fei Liang, Bing Zhao, Xiang Zhu, Chao Zhou, Luis A. J. Mur, Jeremy A. Roberts, Junli Zhang, Xuebin Zhang
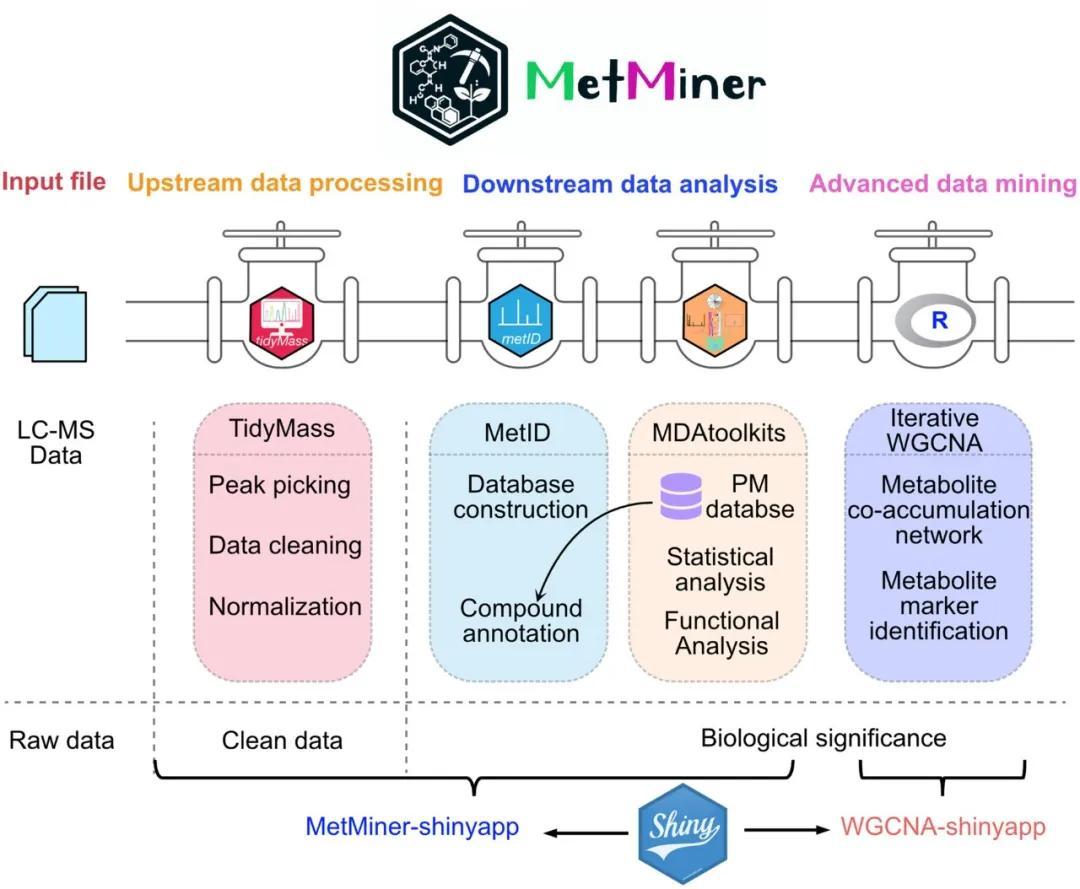
MetMiner, a user-friendly, full-functionality pipeline designed for plant metabolomics data analysis, leverages advanced mass spectrometry data processing frameworks, offering robust data interaction capabilities and efficient data mining methods, enabling wet-lab biologists to more easily handle large-scale metabolomics datasets.
Abiotic Stress Responses
TheLpHsfA2-molecular module confers thermotolerance via fine tuning of its transcription in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenneL.)
Guangjing Ma, Zhihao Liu, Shurui Song, Jing Gao, Shujie Liao, Shilong Cao, Yan Xie, Liwen Cao, Longxing Hu, Haichun Jing, Liang Chen

In perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne), the heat shock factors LpHsfA2/4/5 influence heat tolerance by self-regulating and regulating the expression of the heat-shock protein geneLpHSP18.2and the ascorbate peroxidase geneLpAPX1. Natural variation in theLpHsfA2promoter region leads to differences in heat tolerance in perennial ryegrass germplasm.
Cell and Developmental Biology
Coordination of miR319–TaPCF8 with TaSPL14 orchestrates auxin signaling and biosynthesis to regulate plant height in common wheat
Pingan Hao, Chao Jian, Chenyang Hao, Shujuan Liu, Jian Hou, Hongxia Liu, Haixia Liu, Xueyong Zhang, Huixian Zhao, Tian Li

The wheat microRNA Tae-miR319 negatively regulates plant height by targeting the RNA encoding a transcriptional repressor of genes involved in auxin signaling; haplotypes of this repressor gene are associated with plant height and underwent global breeding selection.
MYB52 negatively regulates ADF9-meditated actin filament bundling in Arabidopsis pavement cell morphogenesis
Tianqi Qiu, Yuanyuan Su, Nannan Guo, Xinyuan Zhang, Pengfei Jia, Tonglin Mao, Xianling Wang

In Arabidopsis, the transcription factor MYB52 represses the expression ofACTIN DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR9, leading to the decrease of actin filament bundles, thereby regulating pavement cell morphogenesis. In themyb52mutant, the ACTIN DEPOLYMERIZING FACTOR9 activity is enhanced, promoting pavement cell morphogenesis.
The OsAGO2–OsNAC300–OsNAPmodule regulates leaf senescence in rice
Shaoyan Zheng, Junyu Chen, Ying He, Jingqin Lu, Hong Chen, Zipeng Liang, Junqi Zhang, Zhenlan Liu, Jing Li, Chuxiong Zhuang

Rice ARGONAUTE 2 binds to the microRNA miR2863c to regulate the expression of the transcription factor geneOsNAC300through DNA methylation, ensuring the correct initiation of leaf senescence. The transcription factor OsNAP initiates the normal onset of senescence, directly or indirectly regulating the expression of senescence-associated genes and chloroplast development.
Regulation of cryptochrome-mediated blue light signaling by the ABI4–PIF4 module
Pengyu Song, Zidan Yang, Huaichang Wang, Fangfang Wan, Dingming Kang, Wenming Zheng, Zhizhong Gong, Jigang Li

The AP2/ERF-family transcription factor ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE 4 interacts with the growth-promoting transcription factor PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4 (PIF4) and the blue light photoreceptors cryptochromes, and post-translationally promotes PIF4 protein accumulation under blue light, thus playing an important role in mediating blue light signaling in Arabidopsis.
Transcriptional regulation of phospholipid transport in cotton fiber elongation by GhMYB30D04–GhHD1 interaction complex
Qingwei Song, Chuanhui Du, Yiyang Xu, Jin Wang, Min Lin, Kaijing Zuo

The cotton transcription factor GhMYB30D04 interacts with the homeodomain-leucine zipper transcription factor GhHD1; the GhMYB30D04- GhHD1 complex enhances the expression of genes related to phospholipid transport and accumulation and thus promotes fiber elongation.
Molecular Physiology
Natural variations inMdNAC18exert major genetic effect on apple fruit harvest date by regulating ethylene biosynthesis genes
Guo Wen, Bei Wu, Yi Wang, Ting Wu, Zhenhai Han, Xinzhong Zhang

Natural variants in the transcription factor geneMdNAC18affect apple fruit harvest date by modulating ethylene biosynthesis. Two single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) inMdNAC18, and SNPs and an insertion/deletion in two ethylene biosynthesis genes constitute a genetic variation network and provide an optimized genomics-assisted prediction model for apple breeding.
A PpEIL2/3–PpNAC1–PpWRKY14 module regulates fruit ripening by modulating ethylene production in peach
Yudi Liu, Wen Xiao, Liao Liao, Beibei Zheng, Yunpeng Cao, Yun Zhao, Ruo-Xi Zhang, Yuepeng Han

The transcription factors PpWRKY14 and PpNAC1 promote ripening during the late stages of fruit development, which is accompanied by decreased expression of two repressors ofPpNAC1.
Anchorene, a carotenoid-derived growth regulator, modulates auxin homeostasis by suppressing GH3-mediated auxin conjugation
Danping Ke, Yinpeng Xie, Haipeng Li, Liqun Hu, Yi He, Chao Guo, Yahui Zhai, Jinggong Guo, Kun Li, Zongyan Chu, Junli Zhang, Xuebin Zhang, Salim Al-Babili, Kai Jiang, Yuchen Miao, Kun-Peng Jia

Anchorene, a carotenoid-derived compound, modulates auxin homeostasis and root development by enhancing levels of the auxin indole-3-acetic acid and repressing auxin conjugation mediated by the auxin-amido synthetase GRETCHEN HAGEN 3, revealing the significant role of apocarotenoids in regulating plant development.
Photosynthesis and Crop Physiology
The genome ofEleocharis viviparaelucidates the genetics of C3–C4 photosynthetic plasticity and karyotype evolution in the Cyperaceae
Hongbing Liu, Hang Zhao, Yanwen Zhang, Xiuli Li, Yi Zuo, Zhen Wu, Kaining Jin, Wenfei Xian, Wenzheng Wang, Weidong Ning, Zijian Liu, Xiaoxiao Zhao, Lei Wang, Rowan F. Sage, Tiegang Lu, Matt Stata, Shifeng Cheng

Eleocharis viviparaprovides a prime model for studying photosynthetic plasticity, as it uses C3 photosynthesis underwater and C4 photosynthesis on land. The assembled genome and dynamic gene expression patterns provide new insights into the genetic basis of this photosynthetic transition, which can contribute to crop improvement and breeding strategies.
Plant Biotic Interactions
The plant terpenes DMNT and TMTT function as signaling compounds that attract Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis) to maize plants
Mengjie Zhao, Shijie Huang, Qingyang Zhang, Yuming Wei, Zhen Tao, Chuanhong Wang, Yibing Zhao, Xinqiao Zhang, Jinghui Dong, Ling Wang, Chen Chen, Tengyue Wang, Peijin Li

Maize plants infested by Asian corn borer larvae produce terpene compounds, termed herbivory-induced plant volatiles, that attract additional corn borer larvae. When the maize genes encoding enzymes involved in biosynthesis of these compounds are knocked out, the maize plants are less attractive to corn borer larvae.
Profiling ofPhakopsora pachyrhizitranscriptome revealed co-expressed virulence effectors as prospective RNA interference targets for soybean rust management
Haibing Ouyang, Guangzheng Sun, Kainan Li, Rui Wang, Xiaoyu Lv, Zhichao Zhang, Rong Zhao, Ying Wang, Haidong Shu, Haibin Jiang, Sicong Zhang, Jinbin Wu, Qi Zhang, Xi Chen, Tengfei Liu, Wenwu Ye, Yan Wang, Yuanchao Wang
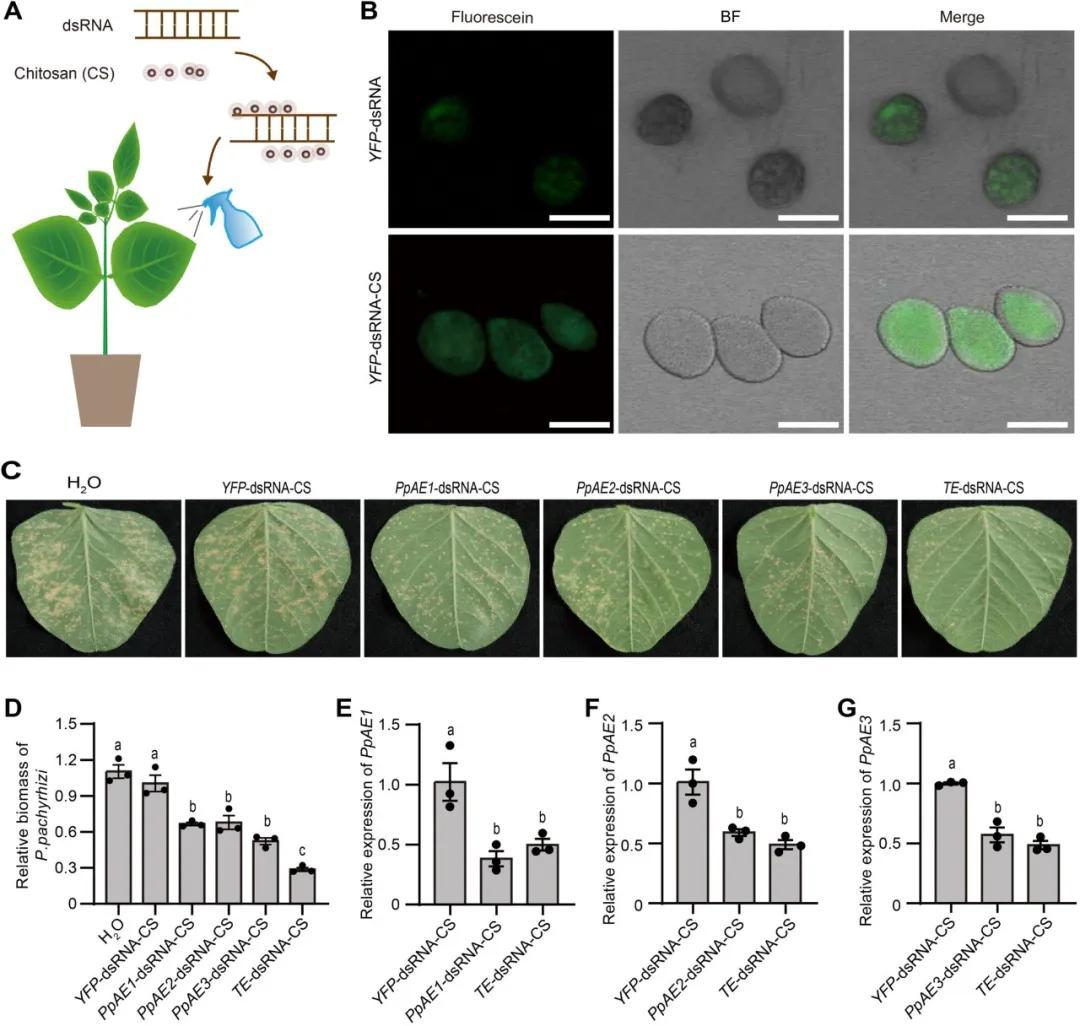
Transcriptome and immunological analysis identified three effector genes of rust fungus as suppressors of plant immune responses, and nanometer nucleic acid pesticides were developed to target them, providing an effective strategy to protect soybean against soybean rust.
Regulation of maize growth and immunity by ZmSKI3-mediated RNA decay and post-transcriptional gene silencing
Jie Gao, Na Zhang, Guohui Liu, Jinjun Tian, Mengyao Chen, Ying Wang, Ye Xing, Ying Zhang, Chenyang Zhao, Xiaohuan Mu, Yanwen Yu, Hongbin Niu, Jiankun Li, Jihua Tang, Mingyue Gou

ZmSKI3 mediates the 3'-5' degradation of RNAs. Knockout of ZmSKI3 leads to enhanced disease resistance and retarded plant growth, and overexpression of ZmSKI3 results in increased disease susceptibility, revealing the sophisticated regulation of plant growth and immunity by ZmSKI3-mediated RNA decay and post-transcriptional gene silencing in maize.
